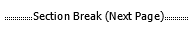
Glossary
| Term | Definition | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
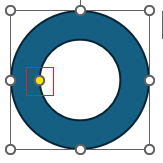
| Adjustment handles | For certain images and graphic visuals when selected a selection frame appears around it including a yellow dot called an adjustment handle. These let you adjust the inner or outer dimensions of that image/graphic. Not to be confused with sizing handles, for more information and examples see here: Altering images and objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Alignment | Where the text sits in the editable area. Four alignment options are available: Left, centre, right and justified. Justified is when the text is aligned to both the right and left margins, creating spaces between words so the paragraph takes up all the space between the margins. You may have seen this in some physical newspapers which justify text in their columns. | |||||||||||||||
| Anchor | Floating images are associated with (or 'anchored' to) a certain paragraph indicated by a small blue anchor in the left margin. If the image is moved far enough up/down the page Word reassigns the anchor to another paragraph. If the paragraph it is anchored to is moved then the image will move with it.
It is also possible to lock an anchor to a paragraph. See more here: Anchoring. |
|||||||||||||||
| Application / App | Known colloquially as an ‘app’, an application is software that helps user to perform particular tasks. For example Microsoft Word is a word processing app, Adobe Photoshop is an image editing app, Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge are web browser apps. You are currently using a web browser application to view this website. | |||||||||||||||
| Attribute (formatting) | An attribute is a formatting characteristic that you can apply to text like bold, italic, word processingfont size, or colour. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoComplete | A feature in Word that suggests automatically completing certain common words or phrases. It appears in grey text. If you press Tab it will be placed on the page saving you having to type it. It can be customised by the user if needed. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoCorrect | A feature in Microsoft Office applications that automatically fixes common typos. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoSave | A feature in Microsoft Office 365 applications that automatically saves your work regularly. | |||||||||||||||
| Automatic grammar checking | Underlines words or sentences in blue to indicate a grammatic error. | |||||||||||||||
| Automatic spell checking | Underlines words in red to indicate a misspelling. | |||||||||||||||
| Bullet list / Bullets | A list format of text where each new line has a bullet dot before it. Useful for condensing information into bitesize points. | |||||||||||||||
| Copy | Copies selected information to the clipboard. Content remains where it is. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + C | |||||||||||||||
| Copy and paste / Copying and pasting | Duplicating content from one location to another. See this article for examples: Copying content | |||||||||||||||
| Clipboard | This is a temporary memory store for copied/cut information, allowing you to paste it elsewhere. There are two types to be aware of:
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Colour palette | A choice of colour attributes to format your text with. | |||||||||||||||
| Columns (MS Word layout) | Allows you to the layout of content on pages into types of columns. | |||||||||||||||
| Column boundary marker | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls the column border of a multi-column table. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Cursor / Pointer | The cursor, also known as the pointer, is the arrow or symbol where your mouse or mousepad is currently pointing. It is used to select system files, menus, buttons, objects and content. In applications the cursor icon can change for different actions.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Cursor keys | The up, down, left and right buttons on your keyboard.

|
|||||||||||||||
| Cut | Copies selected information to the clipboard and removes it from the editable space. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + X | |||||||||||||||
| Cut and paste / Cutting and pasting | Removing content from one location and duplicating it in another. See this article for examples: Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Drag / Click and drag / Clicking and dragging | Holding down left click on your mouse or mousepad and moving the cursor across multiple items, normally to select them together. Release the left click when you’ve got everything you need selected. See examples here: Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Drag and drop / dragging and dropping | With content like text, a shape or image already selected, you left click and hold on that selected content then drag the cursor to a new location which moves the content there. Sometimes cutting and pasting can be easier, especially with large images or large amounts of text. See this article for examples:Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Filename | The title given to a file. You decide the flename when saving a file. Filenames appear alongside a file icon. When viewing files in the details view of a window the filename are shown in a Name column. | |||||||||||||||
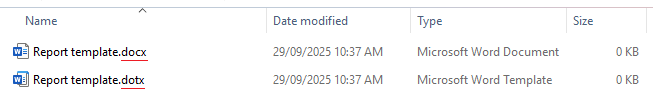
| Filename extension | A suffix at the end of the filename after a full stop/period which indicates a file's file type. E.g. a Word document will have the filename extension .docx while a Excel workbook will have .xlsx.
|
|||||||||||||||
| File type | The format a file is saved in, such as a document, image or video. When viewing files in the details view of a window the file types are shown in a Type column. The file type is also indicated by the Filename extension. | |||||||||||||||
| First-line indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls either where the first line of a paragraph starts or a bullet/number starts in a list. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Floating image | A floating image is one that is able to move freely on the page independent of the text on it. This is set by layout options and wrapping. Floating images have an anchor which links them to a particular paragraph. See the different types of wrap options to make an image float here: Layout options | |||||||||||||||
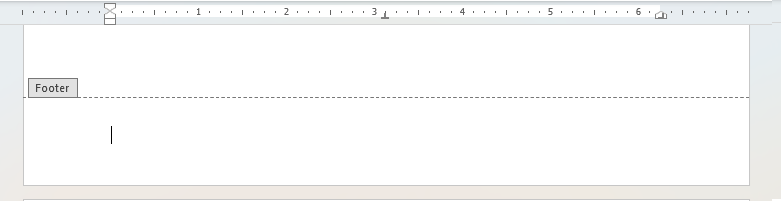
| Footer | Content placed at the bottom of each page to help the reader navigate, identify or understand the context of the page or document. Page numbers for example are usually found in a footer. To access the footer space either double click in the margin at the bottom of the page or go to Insert > Header & Footer > Footer. See more here: Headers and Footers
|
|||||||||||||||
| Font | Font is the typographical design of the text. There are many different fonts you can choose from. Note: Some may not be appropriate for formal documents. | |||||||||||||||
| Format / Formatting | The look and feel of content. See this article on Formatting text. | |||||||||||||||
| Formatting markers | Formatting markers are layout-level controls that affect how content flows, appears or is divided in a document. They are non-printing characters that are invisible by default in Word; to make them visible select File > Show/Hide ¶. Formatting markers include:
Note: Paragraph marks (hard returns), line breaks (soft returns), spaces and tabs are formatting marks. |
|||||||||||||||
| Formatting marks | Formatting marks are a category of non-printing characters that affect the the look and feel of content on the page. In Word they're invisible by default; to make them visible select File > Show/Hide ¶. Formatting marks include:
Note: Page breaks, section breaks and hidden text are not formatting marks, they are formatting markers. |
|||||||||||||||
| Format Painter | A very useful tool that lets you copy the formatting of text to apply it on other text, like copy and paste but for formatting. See this article for more on Formatting text.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Gridlines | The invisible structure of a table that shows the outline of the rows and columns. This helps visualise the table even if no borders are applied (Note: gridlines are not printed, only borders are). The View Gridlines option is found via Table Layout (which only appears when the insertion point is inside a table) > Table. | |||||||||||||||
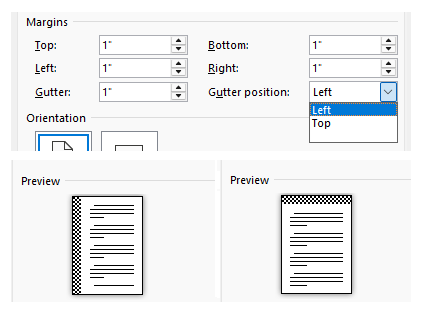
| Gutter / Guttering | Guttering is extra space added to the left side or top margin to allow for physical binding of a document. It's purpose is to ensure content on the page remains visible and isn't swalled up by physical binding when it's applied to the pages (e.g. a book spine, stapling, or hole‑punching). In Word, guttering can be edited in the Page setup dialog which is detailed in this article: Page setup options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Hanging indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls the position of all lines in a paragraph except for the first line. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Hard return | When typing pressing Enter will create a hard return that starts a new paragraph. In lists, it will create a new bullet/list number, see Lists: Soft and hard returns for examples. Another type of return is a soft return. | |||||||||||||||
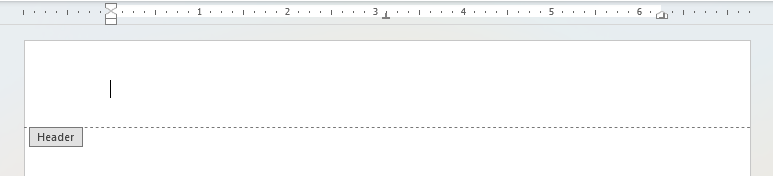
| Header | Content placed at the top of each page to help the reader navigate, identify or understand the context of the page or document. For example a chapter/unit/section title might be something you find in a header. To access the header space either double click on the margin at the top of the page or go to Insert > Header & Footer > Header.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Highlight (formatting) | The highlight tool can be found under Home > Font. It applies a highlight colour behind selected text. | |||||||||||||||
| Highlight (selected content) | When text is selected it will be highlighted with a grey background to show what you have selected. Note: Another kind of highlight exists when formatting text which changes the background colour of text, see Highlight (formatting). | |||||||||||||||
| Indent | Space between a line of content and the margin. You can add indents by pressing Tab or increase and decrease them via Home > Paragraph > Increase/Decrease Indent. The finer details of indents can be controlled by dragging indent markers on the horizontal ruler, see examples in this article: Indents. It is also possible to drag the left margin or right margin beyond the margin of a page, known as a negative margin. | |||||||||||||||
| Indent markers | Indent markers are found on the horizontal ruler when content is selected. Have a look at examples and interactivities in this article: Indents. | |||||||||||||||
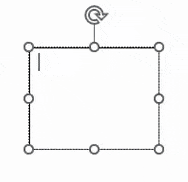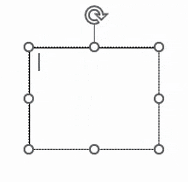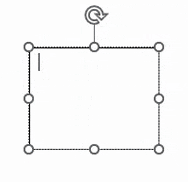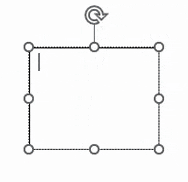
| Insertion point |
A flashing vertical line in an editable area that indicates where you are about to type or edit on the page. You can move this by clicking elsewhere with the cursor or moving it with cursor keys on your keyboard.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Kerning | Kerning is about adjusting the spacing between individual letters in a word to improve visual balance and readability. For example kerning may be used to bring adjacent letters like 'A' and 'V' closer together so they look evenly spaced. Kerning is key to typography in headlines, logos, and display type. If done poorly though kerning can lead to word being misinterpreted, e.g. if you put 'r' and 'n' to close together they can appear like an 'm'.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Left indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls where a paragraph starts, or, in a list where both the bullet/number and content after starts. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Line numbers | Line numbers are numbers against each line in a document, typically used in legal documentation, scripts and technical reviews. You can turn them on in Word via Layout then selecting an option from the Line numbers drop down menu.
Note: You can change where the numbers should and should not apply by 'suppressing' line numbers via Paragraph Options > Line and Page Breaks. |
|||||||||||||||
| Locked anchor | When a floating image is moved far enough up and down a page its anchor will eventually be reassigned to another paragraph. However anchors can be locked to one particular paragraph regardess of where the image is moved to afterwards. This option is in the image's Layout options, see an example here: Locked anchor | |||||||||||||||
| Margin (MS Word) | The space between the edge of the page and the editable area of text. There are margins above, below, left and right of the page and they are editable via options under Layout. | |||||||||||||||
| Maximise screen | An option to enlarge the window/application to take up the whole screen. Typically found on the Quick Access Toolbar at the top of a window/application or from the right-click menu on a taskbar preview. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Office | Known as ‘MS Office’ or just ‘Office’ for short, Microsoft Office is a suite of applications by Microsoft that includes the likes of Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook and others. It is the global standard set of applications used by offices around the world. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Excel | A spreadsheet app in the MS Office suite. Known as Excel for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Outlook | An email and calendar app in the MS Office suite. Known as Outlook for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft PowerPoint | A slideshow presentation app in the MS Office suite. Known as PowerPoint for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Word | A word processing app in the MS Office suite. Known as Word for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Minimise screen | An option to hide the currently open window/application. It can be opened again from the taskbar. Typically found on the Quick Access Toolbar at the top of a window/application or from the right-click menu on a taskbar preview when open. Tip: If you want to minimise all open windows/applications to just see the desktop use the keyboard shortcut Windows + D |
|||||||||||||||
| Multilevel list | A list format of text with its own level of indentation and numbering style. These can be customised as needed. | |||||||||||||||
| Number list | A list format of text where each new line has a sequential number before it. Used primarily for an order of steps in a process. | |||||||||||||||
| OLE object (embedded file) | An OLE object uses Micrsoft's OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) framework to allow an application to display content from an external file, e.g. on a page in Word. OLE objects can be linked to their source with updates in real time or be embedded as a static standalone copy. A full tutorial to OLE objects can be found here: Embedded files (OLE objects)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Operating System (OS) | The operating system (OS for short, a.k.a. system software) manages hardware and runs applications on your computer. Examples of different operating systems are Windows, MacOS (Apple) and Linux. | |||||||||||||||
| Orientation (MS Word) | Which way up the document is: portrait or landscape. Alter the Orientation under the Layout tab on the ribbon. | |||||||||||||||
| Orphan | The first line of a paragraph that appears alone at the bottom of a page detached from the rest of the paragraph on the next page. The opposite of this is a widow. Word prevents these by default but you can disable widow/orphan control in the Line and Pages breaks tab in Paragraph Options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Page break | A page break is the boundary of the editable area between one page and another. To add a page break press Ctrl + Enter. To view page breaks you need to turn on non-printing formatting mark Show/Hide ¶. | |||||||||||||||
| Paste / Pasting | Duplicates information from the clipboard. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + V See these articles for examples of pasting in action: Moving content / Copying content | |||||||||||||||
| Point (font) | Text font size is measure in number metric called points (pt). The larger the point the larger the font. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Access Toolbar | The very top bar above the ribbon, containing tools you may need to use at any time. Top left: Save, Undo and Redo (and Autosave if you're working from OneDrive or SharePoint). Top right: Minimise screen, Maximise screen and Close. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Parts | Building blocks that you can embed on a document with fields for commonly used text like dates, page numbers, names, addresses, titles and keywords. These can be saved to be accessed later. Typically these may be found in templates. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Styles | Styles available in a visual gallery under Home > Styles that you can access and apply to text easily and quickly for frequent use. You can customise the gallery to include other styles as needed.
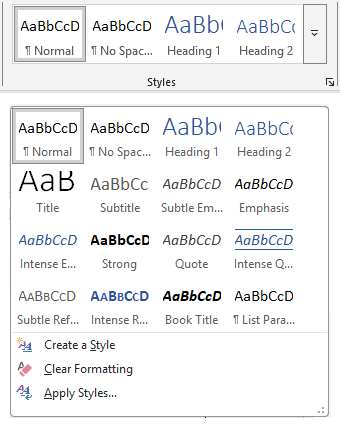 |
|||||||||||||||
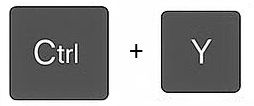
| Redo | Option to repeat the last action. The opposite of undo. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + Y | |||||||||||||||
| Resize / Resizing | Resizing is changing the size of an image or object like a text box. This is done by selecting the image/object and then clicking and dragging the sizing handles i.e. the dots around it when selected. See more here: Altering images and objects.
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Ribbon | The bar across the top containing all the tools to edit your document. Tools are organised by tabs. | |||||||||||||||
| Right indent | The right indent on the horizontal ruler controls how far the content starts from the right margin of the page. It shifts the content e.g. an entire paragraph inward on the page from the right, increase or decreasing the space between the right margin and the content. | |||||||||||||||
| Rotate handle | When an image or object is selected it will have a selection frame around it which sometimes includes a rotate handle depending on what it is. You can hold left click and drag on the rotate handle clockwise or anti-clockwise to freely rotate the image/object as needed. See example here: Altering images, graphic visuals and some objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ruler | The horizontal and vertical rulers measure the physical size of the digitally presented page. It also allows you to alter the left margin, right margin, indent markers, and add tab stops. The ruler is turned on via a checkbox under View > Show.
|
|||||||||||||||
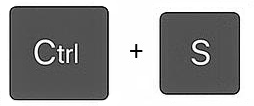
| Save | Saving a file means storing the file's content in its current state onto your computer, cloud drive, or external device. You choose what it's called (the filename) and where it's stored, allowing you to access it later. You also decide what format the file is saved as (the file type); this is indicated by the filename extension. It's good practice to save frequently to avoid losing work due to crashes or power outages. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + S | |||||||||||||||
| Section | Sections are parts of the document where you can change the layout to be different from the rest. This includes the ability to have different page orientation (portrait or landscape), headers and footers, page numbering and margins for example. You can apply section breaks to a document to create and control different sections in it. See more in this article: Section breaks | |||||||||||||||
| Section break | A section break creates a boundary between parts of a document into different sections, allowing different layout compared to the rest of the document. See more in this article: Section breaks | |||||||||||||||
| Select / Selecting / Selection | Choosing text, objects or images by clicking, dragging, or using keyboard shortcuts so that they become active for editing or manipulation. When text is selected, the selected text is highlighted. See this article for different ways to select and examples: Selecting text | |||||||||||||||
| Selection frame | When an image or object is selected a selection frame appears around it with tools to alter it in terms of size, rotation and/or dimensions. Selection frames are discussed more in this article: Altering images and objects | |||||||||||||||
| Sizing handles | When an image or object is selected a selection frame appears around it with dots known as sizing handles. These let you resize the image/object. See examples here: Altering images and objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Soft return | When typing pressing Shift + Enter will create a soft return that starts a new line which is still connected to the same paragraph before known as a line break. In lists, a soft return will create a new line for the existing bullet/list number, see this article for examples: Lists: Soft and hard returns. Another type of return is a hard return. | |||||||||||||||
| Sort | Allows you to arrange content in lists or table columns in ascending or descending order. Custom sort is another option for tables that allows you to sort by multiple criteria. | |||||||||||||||
| Spellcheck (Spelling and grammar) | A tool to review your document for spelling and grammatical errors. | |||||||||||||||
| Status bar | The bar at the bottom of the screen showing details about what you are editing, language setting, accessibility, view options and the zoom tool. E.g. In MS Word the status bar will show the current document’s page number, total pages and word count. | |||||||||||||||
| Style | A set of formatting attributes saved which can be applied to text, e.g. a heading style, table of contents level style, attribution style etc. Styling reduces the amount of work you have to do styling multiple text by just applying the same style each time. | |||||||||||||||
| Tab stop | A tab stop (a.k.a. a 'tab')is a preset location on the horizontal ruler that defines where the insertion point or existing text will align to when you press the Tab key. Tabs are set by clicking onto the horizontal ruler or via the Tabs dialog box (Home > Paragraph > Tabs). | |||||||||||||||
| Table | A structure of rows and columns which can contain content. | |||||||||||||||
| Table border | A visible, styled line applied to the edges of table cells, rows, or columns. Borders can be customized by colour, thickness, and style (e.g., solid, dashed). Note: Borders are printed; gridlines are not. | |||||||||||||||
| Table cell | The intersection of a row and a column in a table. | |||||||||||||||
| Template | A template is a preset file that serves as a starting point for creating new files with consistent formatting, styles and layout. | |||||||||||||||
| Text wrap | This is a function to prevent hyphenation at the end of the line. If your text goes beyond the right margin it will automatically move down to the next line. | |||||||||||||||
| Toggle | A button that lets you switch between one of two options with a single click. For example Autosave in MS Office apps:

|
|||||||||||||||
| Track Changes | This is a tool that when switched on will record any changes you or any other user makes in a document. This is useful for editing and version control. The changes made are then approved or rejected by a reviewer. | |||||||||||||||
| Typo (Typographical error) | An error during typing text, typically a typo is:
|
|||||||||||||||
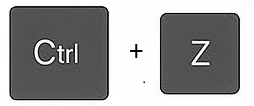
| Undo | A very useful option to reverse your last action. The opposite of redo. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + Z | |||||||||||||||
| Web browser | A web browser is an application used to access and view websites on the internet.. Popular web browsers include Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera. | |||||||||||||||
| Widow | The last line of a paragraph that appears alone at the top of a new page detached from the rest of the paragraph on the page before. The opposite of this is an orphan. Word prevents these by default but you can disable widow/orphan control in the Line and Pages breaks tab in Paragraph Options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Word Document | A Word document is a file created in Microsoft Word that can contain text, formatting, images, shapes, tables, and other elements. It’s where you write, edit, and save your work. Documents have the file extension: .docx (or .doc for older versions). | |||||||||||||||
| Word processing | Writing, editing, and production of documents, such as letters, reports, and books, through the use of a computer program. | |||||||||||||||
| Wrap / Wrapping (images/objects) | Wrapping for images and objects refers to how text flows around or interacts with visual elements like images, shapes, icons, 3D models or charts, or objects like a text box, within a document. It greatly affects readability, general layout and aesthetics. Wrapping can be controlled by an image/object's layout options, more detail and examples on this can be found here: Layout options. |
| Adjustment handles | For certain images and graphic visuals when selected a selection frame appears around it including a yellow dot called an adjustment handle. These let you adjust the inner or outer dimensions of that image/graphic. Not to be confused with sizing handles, for more information and examples see here: Altering images and objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Alignment | Where the text sits in the editable area. Four alignment options are available: Left, centre, right and justified. Justified is when the text is aligned to both the right and left margins, creating spaces between words so the paragraph takes up all the space between the margins. You may have seen this in some physical newspapers which justify text in their columns. | |||||||||||||||
| Anchor | Floating images are associated with (or 'anchored' to) a certain paragraph indicated by a small blue anchor in the left margin. If the image is moved far enough up/down the page Word reassigns the anchor to another paragraph. If the paragraph it is anchored to is moved then the image will move with it.
It is also possible to lock an anchor to a paragraph. See more here: Anchoring. |
|||||||||||||||
| Application / App | Known colloquially as an ‘app’, an application is software that helps user to perform particular tasks. For example Microsoft Word is a word processing app, Adobe Photoshop is an image editing app, Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge are web browser apps. You are currently using a web browser application to view this website. | |||||||||||||||
| Attribute (formatting) | An attribute is a formatting characteristic that you can apply to text like bold, italic, word processingfont size, or colour. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoComplete | A feature in Word that suggests automatically completing certain common words or phrases. It appears in grey text. If you press Tab it will be placed on the page saving you having to type it. It can be customised by the user if needed. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoCorrect | A feature in Microsoft Office applications that automatically fixes common typos. | |||||||||||||||
| AutoSave | A feature in Microsoft Office 365 applications that automatically saves your work regularly. | |||||||||||||||
| Automatic grammar checking | Underlines words or sentences in blue to indicate a grammatic error. | |||||||||||||||
| Automatic spell checking | Underlines words in red to indicate a misspelling. | |||||||||||||||
| Bullet list / Bullets | A list format of text where each new line has a bullet dot before it. Useful for condensing information into bitesize points. | |||||||||||||||
| Copy | Copies selected information to the clipboard. Content remains where it is. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + C | |||||||||||||||
| Copy and paste / Copying and pasting | Duplicating content from one location to another. See this article for examples: Copying content | |||||||||||||||
| Clipboard | This is a temporary memory store for copied/cut information, allowing you to paste it elsewhere. There are two types to be aware of:
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Colour palette | A choice of colour attributes to format your text with. | |||||||||||||||
| Columns (MS Word layout) | Allows you to the layout of content on pages into types of columns. | |||||||||||||||
| Column boundary marker | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls the column border of a multi-column table. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Cursor / Pointer | The cursor, also known as the pointer, is the arrow or symbol where your mouse or mousepad is currently pointing. It is used to select system files, menus, buttons, objects and content. In applications the cursor icon can change for different actions.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Cursor keys | The up, down, left and right buttons on your keyboard.

|
|||||||||||||||
| Cut | Copies selected information to the clipboard and removes it from the editable space. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + X | |||||||||||||||
| Cut and paste / Cutting and pasting | Removing content from one location and duplicating it in another. See this article for examples: Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Drag / Click and drag / Clicking and dragging | Holding down left click on your mouse or mousepad and moving the cursor across multiple items, normally to select them together. Release the left click when you’ve got everything you need selected. See examples here: Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Drag and drop / dragging and dropping | With content like text, a shape or image already selected, you left click and hold on that selected content then drag the cursor to a new location which moves the content there. Sometimes cutting and pasting can be easier, especially with large images or large amounts of text. See this article for examples:Moving content | |||||||||||||||
| Filename | The title given to a file. You decide the flename when saving a file. Filenames appear alongside a file icon. When viewing files in the details view of a window the filename are shown in a Name column. | |||||||||||||||
| Filename extension | A suffix at the end of the filename after a full stop/period which indicates a file's file type. E.g. a Word document will have the filename extension .docx while a Excel workbook will have .xlsx.

|
|||||||||||||||
| File type | The format a file is saved in, such as a document, image or video. When viewing files in the details view of a window the file types are shown in a Type column. The file type is also indicated by the Filename extension. | |||||||||||||||
| First-line indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls either where the first line of a paragraph starts or a bullet/number starts in a list. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Floating image | A floating image is one that is able to move freely on the page independent of the text on it. This is set by layout options and wrapping. Floating images have an anchor which links them to a particular paragraph. See the different types of wrap options to make an image float here: Layout options | |||||||||||||||
| Footer | Content placed at the bottom of each page to help the reader navigate, identify or understand the context of the page or document. Page numbers for example are usually found in a footer. To access the footer space either double click in the margin at the bottom of the page or go to Insert > Header & Footer > Footer. See more here: Headers and Footers
|
|||||||||||||||
| Font | Font is the typographical design of the text. There are many different fonts you can choose from. Note: Some may not be appropriate for formal documents. | |||||||||||||||
| Format / Formatting | The look and feel of content. See this article on Formatting text. | |||||||||||||||
| Formatting markers | Formatting markers are layout-level controls that affect how content flows, appears or is divided in a document. They are non-printing characters that are invisible by default in Word; to make them visible select File > Show/Hide ¶. Formatting markers include:
Note: Paragraph marks (hard returns), line breaks (soft returns), spaces and tabs are formatting marks. |
|||||||||||||||
| Formatting marks | Formatting marks are a category of non-printing characters that affect the the look and feel of content on the page. In Word they're invisible by default; to make them visible select File > Show/Hide ¶. Formatting marks include:
Note: Page breaks, section breaks and hidden text are not formatting marks, they are formatting markers. |
|||||||||||||||
| Format Painter |
Format Painter is a very useful tool that lets you copy the formatting of text to apply it on other text, like copy and paste but for formatting. See more in this article about formatting text. |
|||||||||||||||
| Gridlines | The invisible structure of a table that shows the outline of the rows and columns. This helps visualise the table even if no borders are applied (Note: gridlines are not printed, only borders are). The View Gridlines option is found via Table Layout (which only appears when the insertion point is inside a table) > Table. | |||||||||||||||
| Gutter / Guttering | Guttering is extra space added to the left side or top margin to allow for physical binding of a document. It's purpose is to ensure content on the page remains visible and isn't swalled up by physical binding when it's applied to the pages (e.g. a book spine, stapling, or hole‑punching). In Word, guttering can be edited in the Page setup dialog which is detailed in this article: Page setup options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Hanging indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls the position of all lines in a paragraph except for the first line. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Hard return | When typing pressing Enter will create a hard return that starts a new paragraph. In lists, it will create a new bullet/list number, see Lists: Soft and hard returns for examples. Another type of return is a soft return. | |||||||||||||||
| Header | Content placed at the top of each page to help the reader navigate, identify or understand the context of the page or document. For example a chapter/unit/section title might be something you find in a header. To access the header space either double click on the margin at the top of the page or go to Insert > Header & Footer > Header.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Highlight (formatting) | The highlight tool can be found under Home > Font. It applies a highlight colour behind selected text. | |||||||||||||||
| Highlight (selected content) | When text is selected it will be highlighted with a grey background to show what you have selected. Note: Another kind of highlight exists when formatting text which changes the background colour of text, see Highlight (formatting). | |||||||||||||||
| Indent | Space between a line of content and the margin. You can add indents by pressing Tab or increase and decrease them via Home > Paragraph > Increase/Decrease Indent. The finer details of indents can be controlled by dragging indent markers on the horizontal ruler, see examples in this article: Indents. It is also possible to drag the left margin or right margin beyond the margin of a page, known as a negative margin. | |||||||||||||||
| Indent markers | Indent markers are found on the horizontal ruler when content is selected. Have a look at examples and interactivities in this article: Indents. | |||||||||||||||
| Insertion point |
A flashing vertical line in an editable area that indicates where you are about to type or edit on the page. You can move this by clicking elsewhere with the cursor or moving it with cursor keys on your keyboard. 

|
|||||||||||||||
| Kerning | Kerning is about adjusting the spacing between individual letters in a word to improve visual balance and readability. For example kerning may be used to bring adjacent letters like 'A' and 'V' closer together so they look evenly spaced. Kerning is key to typography in headlines, logos, and display type. If done poorly though kerning can lead to word being misinterpreted, e.g. if you put 'r' and 'n' to close together they can appear like an 'm'.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Left indent | An indent marker found on the horizontal ruler that controls where a paragraph starts, or, in a list where both the bullet/number and content after starts. See examples in this article: Indents | |||||||||||||||
| Line numbers | Line numbers are numbers against each line in a document, typically used in legal documentation, scripts and technical reviews. You can turn them on in Word via Layout then selecting an option from the Line numbers drop down menu.
Note: You can change where the numbers should and should not apply by 'suppressing' line numbers via Paragraph Options > Line and Page Breaks. |
|||||||||||||||
| Locked anchor | When a floating image is moved far enough up and down a page its anchor will eventually be reassigned to another paragraph. However anchors can be locked to one particular paragraph regardess of where the image is moved to afterwards. This option is in the image's Layout options, see an example here: Locked anchor | |||||||||||||||
| Margin (MS Word) | The space between the edge of the page and the editable area of text. There are margins above, below, left and right of the page and they are editable via options under Layout. | |||||||||||||||
| Maximise screen | An option to enlarge the window/application to take up the whole screen. Typically found on the Quick Access Toolbar at the top of a window/application or from the right-click menu on a taskbar preview. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Office | Known as ‘MS Office’ or just ‘Office’ for short, Microsoft Office is a suite of applications by Microsoft that includes the likes of Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook and others. It is the global standard set of applications used by offices around the world. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Excel | A spreadsheet app in the MS Office suite. Known as Excel for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Outlook | An email and calendar app in the MS Office suite. Known as Outlook for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft PowerPoint | A slideshow presentation app in the MS Office suite. Known as PowerPoint for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Microsoft Word | A word processing app in the MS Office suite. Known as Word for short. | |||||||||||||||
| Minimise screen | An option to hide the currently open window/application. It can be opened again from the taskbar. Typically found on the Quick Access Toolbar at the top of a window/application or from the right-click menu on a taskbar preview when open. Tip: If you want to minimise all open windows/applications to just see the desktop use the keyboard shortcut Windows + D |
|||||||||||||||
| Multilevel list | A list format of text with its own level of indentation and numbering style. These can be customised as needed. | |||||||||||||||
| Number list | A list format of text where each new line has a sequential number before it. Used primarily for an order of steps in a process. | |||||||||||||||
| OLE object (embedded file) | An OLE object uses Micrsoft's OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) framework to allow an application to display content from an external file, e.g. on a page in Word. OLE objects can be linked to their source with updates in real time or be embedded as a static standalone copy. A full tutorial to OLE objects can be found here: Embedded files (OLE objects)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Operating System (OS) | The operating system (OS for short, a.k.a. system software) manages hardware and runs applications on your computer. Examples of different operating systems are Windows, MacOS (Apple) and Linux. | |||||||||||||||
| Orientation (MS Word) | Which way up the document is: portrait or landscape. Alter the Orientation under the Layout tab on the ribbon. | |||||||||||||||
| Orphan | The first line of a paragraph that appears alone at the bottom of a page detached from the rest of the paragraph on the next page. The opposite of this is a widow. Word prevents these by default but you can disable widow/orphan control in the Line and Pages breaks tab in Paragraph Options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Page break | A page break is the boundary of the editable area between one page and another. To add a page break press Ctrl + Enter. To view page breaks you need to turn on non-printing formatting mark Show/Hide ¶. | |||||||||||||||
| Paste / Pasting | Duplicates information from the clipboard. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + V See these articles for examples of pasting in action: Moving content / Copying content | |||||||||||||||
| Point (font) | Text font size is measure in number metric called points (pt). The larger the point the larger the font. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Access Toolbar | The very top bar above the ribbon, containing tools you may need to use at any time. Top left: Save, Undo and Redo (and Autosave if you're working from OneDrive or SharePoint). Top right: Minimise screen, Maximise screen and Close. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Parts | Building blocks that you can embed on a document with fields for commonly used text like dates, page numbers, names, addresses, titles and keywords. These can be saved to be accessed later. Typically these may be found in templates. | |||||||||||||||
| Quick Styles | Styles available in a visual gallery under Home > Styles that you can access and apply to text easily and quickly for frequent use. You can customise the gallery to include other styles as needed.
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Redo | Option to repeat the last action. The opposite of undo. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + Y | |||||||||||||||
| Resize / Resizing | Resizing is changing the size of an image or object like a text box. This is done by selecting the image/object and then clicking and dragging the sizing handles i.e. the dots around it when selected. See more here: Altering images and objects.
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Ribbon | The bar across the top containing all the tools to edit your document. Tools are organised by tabs. | |||||||||||||||
| Right indent | The right indent on the horizontal ruler controls how far the content starts from the right margin of the page. It shifts the content e.g. an entire paragraph inward on the page from the right, increase or decreasing the space between the right margin and the content. | |||||||||||||||
| Rotate handle | When an image or object is selected it will have a selection frame around it which sometimes includes a rotate handle depending on what it is. You can hold left click and drag on the rotate handle clockwise or anti-clockwise to freely rotate the image/object as needed. See example here: Altering images, graphic visuals and some objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ruler | The horizontal and vertical rulers measure the physical size of the digitally presented page. It also allows you to alter the left margin, right margin, indent markers, and add tab stops. The ruler is turned on via a checkbox under View > Show.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Save | Saving a file means storing the file's content in its current state onto your computer, cloud drive, or external device. You choose what it's called (the filename) and where it's stored, allowing you to access it later. You also decide what format the file is saved as (the file type); this is indicated by the filename extension. It's good practice to save frequently to avoid losing work due to crashes or power outages. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + S | |||||||||||||||
| Section | Sections are parts of the document where you can change the layout to be different from the rest. This includes the ability to have different page orientation (portrait or landscape), headers and footers, page numbering and margins for example. You can apply section breaks to a document to create and control different sections in it. See more in this article: Section breaks | |||||||||||||||
| Section break | A section break creates a boundary between parts of a document into different sections, allowing different layout compared to the rest of the document. See more in this article: Section breaks | |||||||||||||||
| Select / Selecting / Selection | Choosing text, objects or images by clicking, dragging, or using keyboard shortcuts so that they become active for editing or manipulation. When text is selected, the selected text is highlighted. See this article for different ways to select and examples: Selecting text | |||||||||||||||
| Selection frame | When an image or object is selected a selection frame appears around it with tools to alter it in terms of size, rotation and/or dimensions. Selection frames are discussed more in this article: Altering images and objects | |||||||||||||||
| Sizing handles | When an image or object is selected a selection frame appears around it with dots known as sizing handles. These let you resize the image/object. See examples here: Altering images and objects
|
|||||||||||||||
| Soft return | When typing pressing Shift + Enter will create a soft return that starts a new line which is still connected to the same paragraph before known as a line break. In lists, a soft return will create a new line for the existing bullet/list number, see this article for examples: Lists: Soft and hard returns. Another type of return is a hard return. | |||||||||||||||
| Sort | Allows you to arrange content in lists or table columns in ascending or descending order. Custom sort is another option for tables that allows you to sort by multiple criteria. | |||||||||||||||
| Spellcheck (Spelling and grammar) | A tool to review your document for spelling and grammatical errors. | |||||||||||||||
| Status bar | The bar at the bottom of the screen showing details about what you are editing, language setting, accessibility, view options and the zoom tool. E.g. In MS Word the status bar will show the current document’s page number, total pages and word count. | |||||||||||||||
| Style | A set of formatting attributes saved which can be applied to text, e.g. a heading style, table of contents level style, attribution style etc. Styling reduces the amount of work you have to do styling multiple text by just applying the same style each time. | |||||||||||||||
| Tab stop | A tab stop (a.k.a. a 'tab')is a preset location on the horizontal ruler that defines where the insertion point or existing text will align to when you press the Tab key. Tabs are set by clicking onto the horizontal ruler or via the Tabs dialog box (Home > Paragraph > Tabs). | |||||||||||||||
| Table | A structure of rows and columns which can contain content. | |||||||||||||||
| Table border | A visible, styled line applied to the edges of table cells, rows, or columns. Borders can be customized by colour, thickness, and style (e.g., solid, dashed). Note: Borders are printed; gridlines are not. | |||||||||||||||
| Table cell | The intersection of a row and a column in a table. | |||||||||||||||
| Template | A template is a preset file that serves as a starting point for creating new files with consistent formatting, styles and layout. | |||||||||||||||
| Text wrap | This is a function to prevent hyphenation at the end of the line. If your text goes beyond the right margin it will automatically move down to the next line. | |||||||||||||||
| Toggle | A button that lets you switch between one of two options with a single click. For example Autosave in MS Office apps:

|
|||||||||||||||
| Track Changes | This is a tool that when switched on will record any changes you or any other user makes in a document. This is useful for editing and version control. The changes made are then approved or rejected by a reviewer. | |||||||||||||||
| Typo (Typographical error) | An error during typing text, typically a typo is:
|
|||||||||||||||
| Undo | A very useful option to reverse your last action. The opposite of redo. Keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + Z | |||||||||||||||
| Web browser | A web browser is an application used to access and view websites on the internet. Popular web browsers include Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera. | |||||||||||||||
| Widow | The last line of a paragraph that appears alone at the top of a new page detached from the rest of the paragraph on the page before. The opposite of this is an orphan. Word prevents these by default but you can disable widow/orphan control in the Line and Pages breaks tab in Paragraph Options
|
|||||||||||||||
| Word Document | A Word document is a file created in Microsoft Word that can contain text, formatting, images, shapes, tables, and other elements. It’s where you write, edit, and save your work. Documents have the file extension: .docx (or .doc for older versions). | |||||||||||||||
| Word processing | Writing, editing, and production of documents, such as letters, reports, and books, through the use of a computer program. | |||||||||||||||
| Wrap / Wrapping (images/objects) | Wrapping for images and objects refers to how text flows around or interacts with visual elements like images, shapes, icons, 3D models or charts, or objects like a text box, within a document. It greatly affects readability, general layout and aesthetics. Wrapping can be controlled by an image/object's layout options, more detail and examples on this can be found here: Layout options. |